Janthinobacterium lividium is a gram negative purple pigmented bacteria that has been found by rivers, springs, and lakes all over the world.
References:
Schloss PD, Allen HK, Klimowicz AK, Mlot C, Gross JA, Savengsuksa S, McEllin J, Clardy J, Ruess RW, Handelsman J. Psychrotrophic Strain of Janthinobacterium lividum from a Cold Alaskan Soil Produces Prodigiosin. 2010 [accessed 2017 Mar 30];29. http://resolver.ebscohost.com/openurl?sid=google&auinit=PD&aulast=Schloss&atitle=Psychrotrophic strain of Janthinobacterium lividum from a cold Alaskan soil produces prodigiosin&id=doi:10.1089/dna.2010.1020&title=DNA and cell biology&volume=29&issue=9&date=2010&spage=533
Pantanella F, Berlutti F, Passariello C, Sarli S, Morea C, Schippa S. Violacein and biofilm production in Janthinobacterium lividum. 2006 Jul 24 [accessed 2017 Mar 30]. http://resolver.ebscohost.com/openurl?sid=google&auinit=F&aulast=Pantanella&atitle=Violacein and biofilm production in Janthinobacterium lividum&id=doi%3a10.1111%2fj.1365-2672.2006.03155.x&title=Journal of Applied Microbiology&volume=102&issue=4&date=2007&spage=992&site=ftf-live
Brucker RM, Harris RN, Schwantes CR, Gallaher TN, Flaherty DC, Lam BA, Minbiole KPC. Amphibian Chemical Defense: Antifungal Metabolites of the Microsymbiont Janthinobacterium lividum on the Salamander Plethodon cinereus. 2008 Oct 24 [accessed 2017 Mar 30]. http://resolver.ebscohost.com/openurl?sid=google&auinit=RM&aulast=Brucker&atitle=Amphibian chemical defense: antifungal metabolites of the microsymbiont Janthinobacterium lividum on the salamander Plethodon cinereus&id=doi:10.1007/s10886-008-9555-7&title=Journal of Chemical Ecology&volume=34&issue=11&date=2008&spage=1422
Date Collected: February 2, 2017
Methods for Isolation and Identification:
- Sample was taken from the river bank of the Appomattox River it was then washed and spun with sterile water, and spread on an agar plate. It was then incubated at 30 degrees Celsius for 96 hours.
- A purple colony was selected for gene sequencing by PCR amplification.
- The PCR product was digested with MspI and sequenced to identify the genus and species of the bacteria.

Figure 1. Appomattox River

Figure 2. Soil collection site from the Appomattox River.

Figure 3. Sample bacteria used (circled in blue).
Results:
- MspI Digestion (Figure 4.): A 900 bp product was amplified by PCR. Upon digestion with MspI, two bands appeared under 250 bp and at 500 bp were identified.
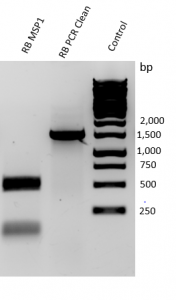
Figure 4. Results of PCR amplification and MspI digestion
Sequence Analysis (Figure 5): The sequenced PCR product generated 892 bases of high-quality reads that were used to identify the genus and species of the colony. NCBI BLAST analysis revealed that 99% identify with the bacteria Janthinobacterium lividium.

Figure 5. NCBI BLAST analysis of colony RB-5
Contributed by: Aryana DiPippa, BIOL 250 Spring 2017, Group 5