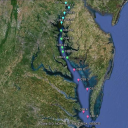
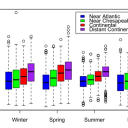
“Spatial Analysis of Potential Risk Factors Associated with Addition of Atlantic Coast Pipeline Through Virginia”
Rachel C. Lombardi, author Introduction Over 728 billion cubic meters (bcm) of dry natural gas was consumed in the United States (U.S.) in 2013, and 24% of U.S. household energy is produced by natural gas (USEIA, 2013; Jaramillo et al., 2007). Due to a growing demand for natural gas, Dominion Inc., in partnership with Duke … Continue reading →