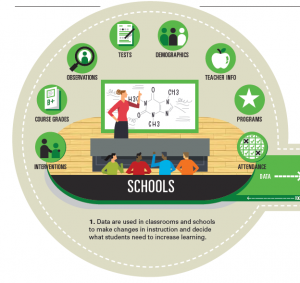
Tips:
Make data an ongoing cycles of instructional improvement
- Routinely use data to guide instructional decisions and to help meet the needs of students
Collect and prepare a variety of data about students
- State assessments
- District benchmarks
- Classroom performance testing
- Child study data
- Other relevant sources
Interpret data and develop a hypothesis about how to improve student outcomes
- Identify strengths and weaknesses of classes and individual students
Modify the instruction to test the hypothesis
- examine instructional practices that may support the implementation of hypothesis
Review new data to determine if improvement has taken place
- Continuously assess learning and review data to drive instruction
- If hypothesis is proven null, re-evaluate data and create a new hypothesis
- If hypothesis is proven true, continue implementing instruction, increasing rigor as students progress