Pseudomonas tolaasii is a whitish/clear, circular bacterial colony that can be found in the Buffalo Creek water.
References:
- Young JM, Saddler GS, Takikawa Y, De Boer SH, Vauterin L, Gardan L, Gvozdyak RI, Stead DE. Names of plant pathogenic bacteria 1864-1995. Rev. Plant Pathol. 1996. 75: 721-763.
Date Collected: February 8, 2017
Methods for Isolation and Identification:
- A water sample was taken from the top of the water of the Buffalo Creek (Figure 1). 100μl of the sample was placed on an agar plate and was incubated at 25 degrees Celsius for 48 hours. The plate was parafilmed and placed in the refrigerator for seven days.
- A whitish/clear, circular colony (Figure 2) was selected for 16S rRNA gene sequencing by PCR amplification.
- The PCR product was sent for DNA sequencing to identify the species of the bacteria.

Figure 1. site of collection (Buffalo Creek)

Figure 2. Selected colony for identification
Results:
- Msp1 digestion (figure 3): A light band was produced at about 770 bp by PCR.
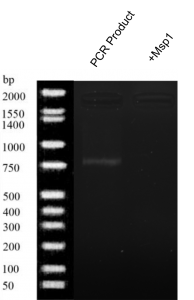
Figure 3. Gel electrophoresis results of Buffalo Creek water PCR product and + MSP1.
- DNA sequence: The sequenced PCR product produced 783 quality base pairs that were used to identify the bacteria as Pseudomonas tolaasii. The chromatogram of the sequence is available as a pdf (HMX3_PREMIX_JF7561_29). NCBI BLAST revealed 99% similarity with 2 gaps out of 783 base pairs (Figure 4).

Figure 4. NCBI BLAST results of chosen colony.
Contributed by: Megan Bland and Hannah Hatke, BIOL 250 Spring 2017