Bacillus cereus is a gram-positive aerobic bacteria that is motile. This off-yellow bacteria is known for causing food poisoning and eye infections, giving rise to non-gastrointestinal infections. It can be found in several different environments due to its ability to live in extremely warm, dry, cold, and radiated condtions.
References:
Bottone, EJ. Bacillus cereus, a Volatile Human Pathogen. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 2010 [accessed 2017 Mar 30];23(2):382–398.
Date collected: February 9, 2017
Methods
- Soil was collected from a site at Lancer Park (Fig. 1). A shovel was used to gather the soil from varying depths, ( 0, 6, and 12 inches), before being placed in a sterile tube. It was then spread on an agar plate. The bacteria were allowed to proliferate at room temperature (23 C) for 18-24 hours. A yellow colony was selected for 16S rRNA gene sequencing via PCR amplification (Fig. 2). The products were then digested with MspI and sequenced for identification.

Fig. 1. Site of soil sample collections
Figure 2: Colony Identified from Sample
Results
PCR amplification and MspI Digest
- A 1,512 bp PCR product was amplified by PCR. Once digested with MspI, four bands were identified: 150 bp, 200 bp, 450 bp, and 700 bp (Fig.3).
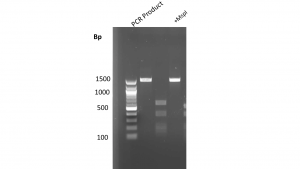
Figure 3: PCR amplification and MspI Digest
Sequencing Analysis:
- The PCR product produced 1512 bases of high-quality data that was used to identify the colony. pdf “http://blogs.longwood.edu/pecmicrobes/files/2017/03/rDNA_seq_1_PREMIX_KG2496_1.pdf“
- The NCBI BLAST analysis showed that there is a 100% match with all 1512 bases of the 16s rRNA gene of Bacillus cereus (Fig. 4).
Figure 4: Sequence Analysis of Colony 2-1
Contributions by:
Juwairyah Gunter, Christina Bell, BIOL 250 Spring 2017, Group 2
