Bacillus pumilus is a gram-positive motile purple pigmented bacteria that has been found from penaeid shrimp that is resistant to marine pathogens.
References:
- J E Hill, J C F Baiano, A C Barnes, Isolation of a novel strain of Bacillus pumilus from penaeid shrimp that is inhibitory against marine pathogens; Journal of Fish Diseases, 2009, Vol 32:1007-1016
Date Collected: February 9, 2017
Methods for Isolation and Identification:
- A soil sample was collected 11.1 inches into Buffalo Creek (Figure 1). A nutrient broth was added to the sample and it was spread onto an LB Agar using a sterile hockey stick. The agar was incubated at 30 degrees Celsius.
- A small purple colony (Figure 2) was selected for 16S rRNA gene sequencing by PCR amplification.
- The PCR product was digested and sequenced in order to identify the bacteria.

Figure 1. Collection site
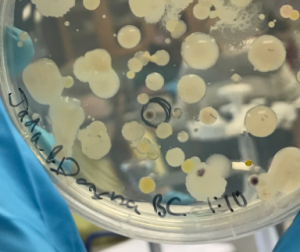
Figure 2. Selected colony
Results:
- MspI digestion (Figure 3) : The amplification of our PCR product was about 1500 bp long. Upon digestion with MspI, about 3 bands appeared at about 500 bp, 350 bp, and 200 bp were identified.
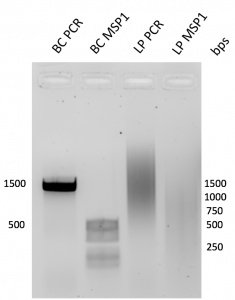
Figure 3. Gel electrophoresis of PCR amplification and MspI digestion
- Sequence Analysis (Figure 4): The PCR product generated 1167 bases of high quality reads. NCBI Blast analysis revealed that 98% identify with the bacteria Bacillus pumilus.
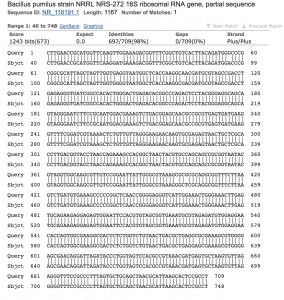
Figure 4. NCBI Blast analysis of colony 13A
mkn7c Contributed by: Dayna Rouse and Jada Russell, BIOL 250 Spring 2017, Group 13